How to Build an AI Agent that Solves Your Daily Office Problems
Gone are the days when you would spend hours each day replying to emails, entering hundreds of rows of data manually, and repeating the same repetitive tasks. Today, we outsource these tasks to Agentic AI tools to save time and effort.
The magic of an AI agent is that you can program it to do any required task in a matter of time.
Agentic means having the capacity to act independently, make decisions, and influence outcomes without constant external direction. Add AI to it, voila! You built an automated agent, but be sure to identify the problem beforehand and how you would solve it before planning the design, training the model, and running it successfully, so you don't waste time.
Let’s understand everything about AI agents and the complete process of building one.
What Does an AI Agent Do?
An AI agent, or Agentic AI, is equivalent to thousands of human assistants; that is, it is quicker and more accurate. It looks at data, understands what is happening, and takes the right action, all without you having to do the work.
For example, if you prompt ChatGPT to create an Excel sheet with 10,000 rows of random customer sales data from Walmart to test for data analysis, it will create an unbelievable list within a few seconds.
Here is the step-by-step process of how an AI agent works.
|
Stage |
What It Does |
How It Helps |
|
1. Understands the Situation or User Input |
Interprets text, voice, images, or data to understand the user's needs. |
Ensures the AI clearly identifies the problem before acting. |
|
2. Thinks Using Data and Rules |
Processes information using logic, algorithms, or predefined guidelines. |
Applies reasoning and domain knowledge to choose the right approach. |
|
3. Learns from Experience or Feedback |
Continuously improves decisions based on new data or user responses. |
Becomes more accurate and context-aware over time. |
|
4. Acts to Complete a Goal |
Executes tasks such as sending messages, scheduling actions, or generating reports. |
Translates thinking into real-world action. |
|
5. Communicates Naturally with People or Other Systems |
Interacts using human-like conversation or API integration. |
Builds trust and enables collaboration between humans and machines. |
Steps to Build an AI Agent That Solves Your Problem
Building an AI agent might sound complex, but when broken into steps, it becomes a very simple and logical process.
Let’s go through each stage from identifying your problem to maintaining your smart digital helper.
Step 1: Know What Problem You Want to Solve
Before you build anything, you need to know what problem your AI agent should fix. Many projects fail because people start coding without a clear goal.
You don’t need an AI agent “just because it’s cool or it is trendy nowadays.” You need one if you really need to solve your pain point.
For example,
- If you spend hours replying to the same customer questions, your AI agent could become a chatbot.
- If you manually sort and filter data, your AI agent could do it in seconds.
- If you track inventory, your AI agent could automatically predict stock needs.
So, write down exactly what the problem is that frustrates you and how an AI helper could make it easier.
The better you define your problem, the better your AI agent will work.
Steps to define your problem
- List repetitive or time-consuming tasks that slow your daily productivity.
- Gather and organize quality data for your AI to learn from.
- Define your main goal. For example, saving time, reducing errors, or gaining insights.
- Visualize the exact goal clearly, like saving 3 hours or cutting errors by 40%.
- Start small with one project to test the results and plan gradual expansion later.
Step 2: Plan the Blueprint to Design Your AI Agent
Now that you know what problem to solve, the next step is to design how your AI agent will work.
For that, you need to know what your AI will do, what data it will use, and what result it should give.
There are different kinds of AI agents, from simple ones that react quickly to smart ones that learn and adapt.
Types of AI agents
- Simple Reflex Agent: It reacts to direct commands (e.g., turn on lights when it is dark).
- Model-Based Agent: It remembers past data and uses it for better decisions.
- Goal-Based Agent: It works toward a specific goal (e.g., reduce customer waiting time).
- Learning Agent: It improves over time using new data and feedback.
If you want your AI to keep getting smarter, choosing a learning agent will be a good choice.
When planning your AI agent
- Decide what data it will use (text, images, numbers, etc.).
- Choose tools and frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, or LangChain.
- Sketch out how users will interact with it. For example, chat, button, or voice.
- Plan how it will connect with other tools or apps.
- Make sure it follows privacy and security rules if it uses real user data.
Step 3: Build and Train Your AI Agent
To know how to do its job, your AI agent needs to see examples, learn from them, and improve over time.
Training involves machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP).
ML teaches your AI how to recognize patterns from data, while NLP helps it understand and respond to human language.
Steps to train your AI agent
- Collect Data: Gather sufficient, relevant examples or datasets related to your plan.
- Clean the Data: Remove errors, duplicates, and irrelevant information so your AI learns from high-quality inputs only.
- Pick a Model: Choose the best algorithm —such as neural networks or decision trees —based on your problem’s complexity.
- Train the Model: Feed the cleaned dataset into your chosen model to help it accurately identify useful patterns.
- Test It: Evaluate your trained AI on new data to measure its accuracy and real-world performance.
- Improve It: Adjust parameters, upgrade with more robust data, and refine performance until results meet the desired goals.
Step 4: Add Tools
Your AI now has a brain. However, it needs a body to interact with people or systems. This is where you integrate it with tools, apps, or websites.
For example,
- You can connect a chatbot AI to your website to answer questions.
- You can link an AI scheduling agent to Google Calendar to book meetings.
- You can connect your AI to social media to automatically reply to messages.
Common tools and platforms to use
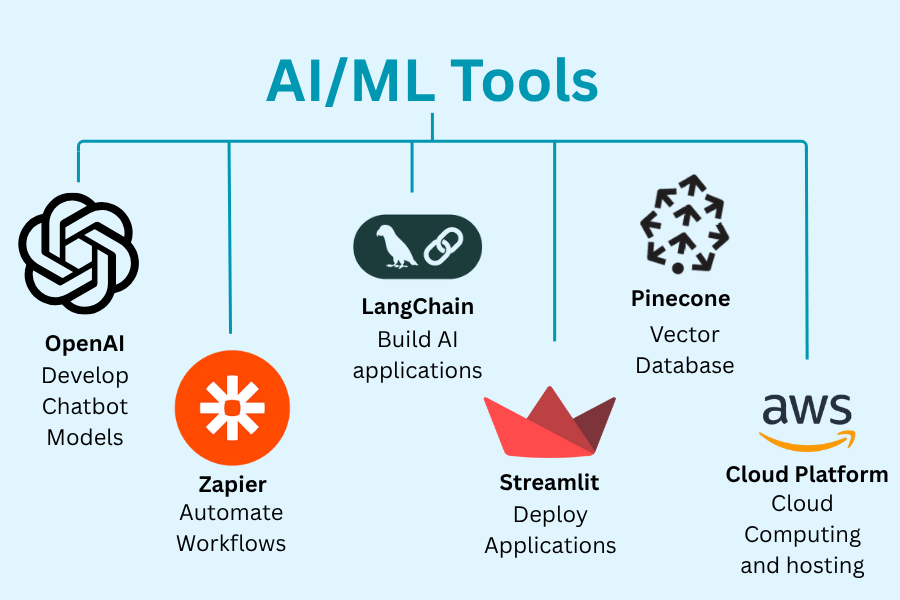
- LangChain: It helps to build reasoning and decision-making pipelines.
- OpenAI Function Calling: It allows your AI to execute real-world tasks automatically through function-based interactions.
- Pinecone/FAISS: It provides vector databases that help your AI recall, search, and leverage past data efficiently.
- Zapier or Make: It automates workflows between your AI system and various web applications for smoother task execution.
- Streamlit or Flask: It enables the easy creation of user-friendly dashboards or interfaces for direct interaction with your AI.
- AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud: It offers reliable hosting, scalability, and powerful cloud infrastructure to deploy and manage AI systems.
Moreover, while integrating these tools, it will be best by
- Keeping the design simple and easy to use.
- Adding “memory” so your AI remembers conversations or data.
- Protecting private information with encryption.
- Letting users provide feedback to improve the AI over time.
Step 5: Test, Improve, and Launch Your AI Agent
Testing is what separates a good AI from a failed one. Before launching your AI agent, test it thoroughly to ensure it works properly.
Check if it truly solves the problem, gives correct answers, and can handle unexpected inputs. This step helps you find and fix errors early, so your AI performs smoothly in real-world situations.
Testing steps
- Unit Testing: Check that every small part of your AI works correctly before combining them.
- User Testing: Let real users try your AI and share feedback about its usefulness and accuracy.
- Stress Testing: Test how well your AI performs when many users use it simultaneously.
- Ethical Check: Ensure your AI delivers fair, safe, and unbiased results for every user.
- Final Launch: Once tests pass, deploy your AI seamlessly across your website, mobile app, or enterprise system.
Deployment tips
- Choose Reliable Hosting: Use trusted platforms like AWS, Azure, or Hugging Face to run your AI.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly check your AI’s speed, accuracy, and behavior using simple performance dashboards.
- Include Human Oversight: Let humans review important AI decisions to prevent mistakes and ensure safe outcomes.
- Update Regularly: Keep adding new data and retraining your AI to keep it accurate and smart.
Step 6: Maintain, Monitor, and Grow Your AI Agent
Like every system, your AI agent must be maintained, updated, and retrained to stay useful.
Over time, data changes, and user behavior evolves. If you don’t keep your AI updated, it can give outdated or wrong results.
How to maintain and improve your AI
- Watch its performance regularly through analytics dashboards.
- Retrain it with new and fresh data.
- Log user interactions to find patterns or problems.
- Fix bugs or wrong outputs as soon as they appear.
- Use cloud platforms for automatic updates and scaling.
- Listen to user feedback.
Conclusion
Building an AI agent is one of the smartest ways to make your daily tasks easier and more efficient.
With the right tools and clear planning, creating an AI agent not only saves you time and effort but also helps to focus on what really matters.
So, ready to build your own smart assistant? Get in touch with Searchable Design, the best data-driven company in Urbandale today, and bring your AI idea to life.
Related Post
RECOMMENDED POSTS
API-Centric Architecture: The Present & Future of SaaS
06, Feb, 2026
RECOMMENDED TOPICS
TAGS
- artificial intelligence
- agentic ai
- ai
- machine learning
- deepseek
- llm
- saas
- growth engineering
- ai/ml
- chatgpt
- data science
- gpt
- openai
- ai development
- gcp
- sql query
- data isolation
- db expert
- database optimize
- customer expectation
- sales growth
- cloud management
- cloud storage
- cloud optimization
- aws
- deep learning
- modular saas
- social media
- social media marketing
- social influencers
- api
- application
- python
- software engineering
- scalable architecture
- api based architecture
- mobile development
- bpa
- climate change
- llm models
- leadership
- it development
- empathy
- static data
- dynamic data
- ai model
- open source
- xai
- qwenlm
- database management
- automation
- healthcare
- modern medicine
- growth hacks
- data roles
- data analyst
- data scientist
- data engineer
- data visualization
- productivity
- artificial intelligene
- test
ABOUT
Stay ahead in the world of technology with Iowa4Tech.com! Explore the latest trends in AI, software development, cybersecurity, and emerging tech, along with expert insights and industry updates.





Comments(0)
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *