
Is Business Process Automation the Key to the Next Industrial Revolution?
Imagine running a sales department buried in repetitive tasks like data entry, filing invoices, email follow-ups, answering phones, and doing paperwork. It does not sound very inspiring because you focus your team and energy on menial tasks instead of drawing funnels to attract more leads, charting out sales plans, testing CTAs and landing pages, or testing out a new sales script, which tends to be exciting and productivity-driven!
The good thing is that automation will optimize your business processes, allowing you to invest more time in creating and testing ideas. Business Process Automation (BPA) is a set of tools and scalable models that help streamline workflows, reduce workload, automate repetitive tasks, create and test Minimum Viable Products (MVPs), and provide purpose-based software to empower teams.
It may be the next industrial revolution, significantly enabling machine learning to overcome human shortcomings. Continue reading this article to learn how you can best utilize BPA.
What is Business Process Automation (BPA)?
Business Process Automation (BPA) involves using AI/ML-powered tools, software, and models to streamline and automate rule-based tasks and workflows, including email follow-up, creating boilerplate codes, testing MVPs, reviewing products for compliance, and even shortlisting interview candidates; therefore, it can be implemented across departments.
BPA helps businesses identify and eliminate bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and reduce waste. A survey reported that organizations lose $1 million in waste every 20 seconds.
For example, tools like UiPath and Zapier help connect different systems, automatically execute workflows, and reduce human error to improve consistency, speed, and productivity. When employees are taken off menial tasks to perform high-value operations, such as planning and development, they feel inspired and rewarded.
Research indicates that organizations implementing end-to-end Business Process Automation (BPA) can reduce operational costs by up to 30% and decrease process time by 50%.
Read on if you are an organization struggling to streamline your business operations.
Why Should Enterprises, Small or Large, Adopt BPA?
Automation is the key to empowering teams to perform better, no matter their size or number. From Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to handling mundane tasks to software making predictive decisions, automation is branching inside all aspects of business operation, empowering teams and growth.
- Automates repetitive tasks to free up employee focus.
- Reduces errors by 80% and accelerates tasks 70% faster on average.
- Standardizes workflows and data handling across departments.
- Reduces total cost of ownership by eliminating repetitive tasks.
- Enhances accuracy using deterministic workflow engines and machine learning models.
- Reduces burnout and allows teams to have more time for creative problem-solving.
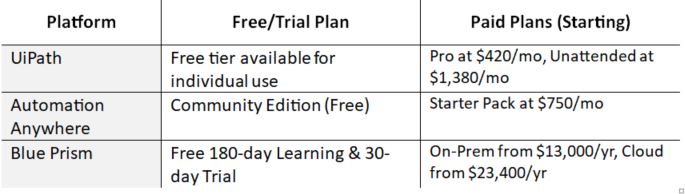
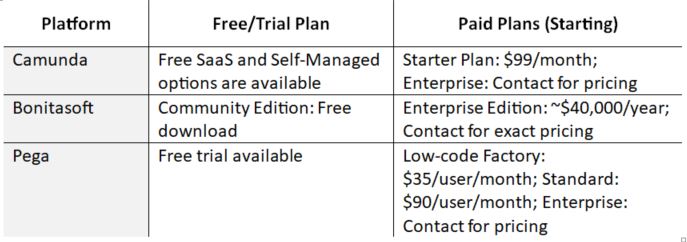
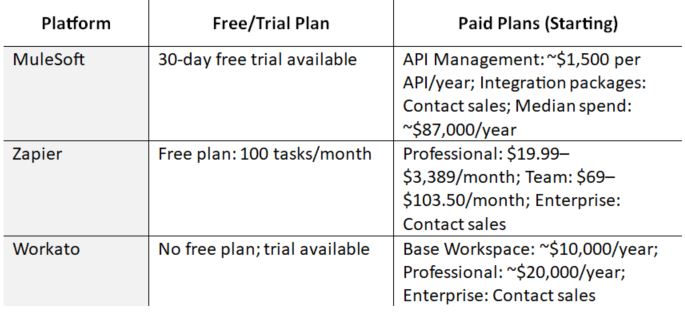
However, adopting BPA may not come cheap. Tools like BasicOps offer free plans with limited functionality, which is suitable for a small team to organize and manage projects, tasks, and meeting notes. Depending on your needs, you can integrate purpose-based Applied AI tools like ProcessMaker, FlowForma, Retool, and Zapier to strengthen high-impact areas.
For enterprises, applying AI tools with customized paid plans may be beneficial in reducing costs, streamlining assembly lines, improving departmental accuracy, and enhancing the customer experience.
How BPA Empowers Your Team & Growth
Let’s delve into BPA-driven models, tools, and techniques, and explore how they can enhance the efficiency of your business processes and team productivity.
1. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA simulates user behavior across systems and interfaces, mimicking human actions such as clicking, copying, and inputting, thereby reducing manual labor in structured tasks.
RPA is ideal for industries such as banking, insurance, retail, and healthcare, where high-volume, repetitive tasks are common.
- Best For: Invoice processing, human resource onboarding, system ticket triage.
- Benefits: Quick to deploy, cost-effective, works with legacy systems.
2. Intelligent Automation (IA)
IA integrates artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities into Robotic Process Automation (RPA). It reads emails, contracts, and handles unstructured data to support informed decision-making.
It enhances workflows with adaptability and cognitive intelligence.
IA benefits sectors such as finance, legal, logistics, and telecom by handling unstructured data, making informed decisions, and continually learning.

- Use Cases: Claims processing, sentiment analysis, predictive maintenance.
- Key Components: Natural Language Processing (NLP), Optical Character Recognition (OCR), and machine learning (ML) models.
3. Business Process Management Systems (BPMS)
The business process management system model executes, monitors, and optimizes enterprise processes in real-time.
BPMS is commonly used in enterprise-level organizations, especially in manufacturing, finance, and government services, to create end-to-end visibility and control over core operations.
- Tech Features: Business process and notation modeling, decision engines, case management.
- Integration: Representational State Transfer APIs, SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) services, middleware connectors.
4. API-Based Automation
API-based systems automate tasks on the back end by communicating with external or internal services.
It is ideal for tech startups, SaaS platforms, and e-commerce businesses seeking to integrate multiple systems and automate workflows in real-time.
- Use Cases: Data syncing, event-triggered actions, customer relationship management software updates.
- Benefits: Fast, reliable, and perfect for microservices architectures.
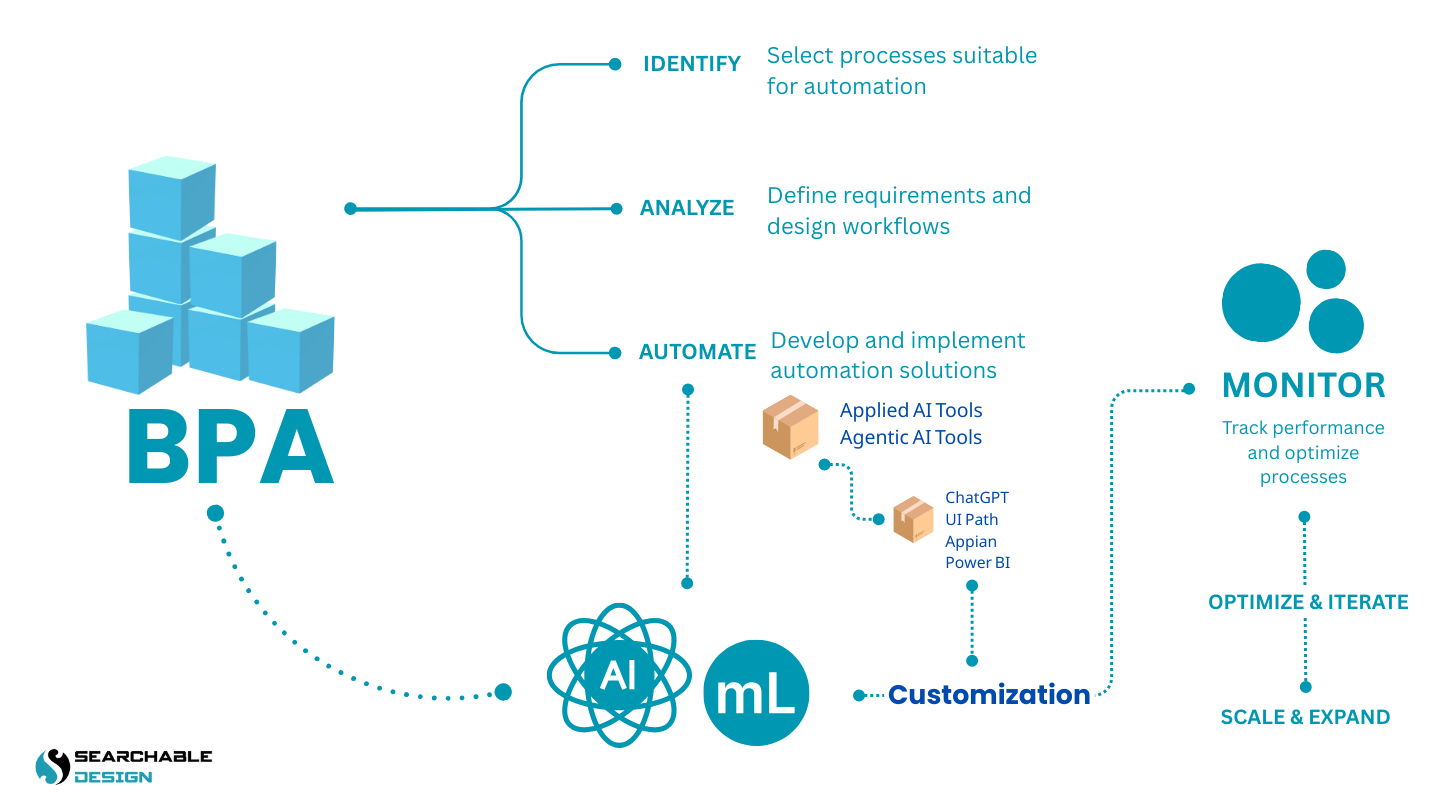
Roadmap to Build Your Automation Journey
Just as constructing a building requires architectural planning, solid foundations, and the right tools, automation necessitates the same approach. Implementing BPA is more than just selecting tools; it involves a project-based lifecycle that spans discovery, development, deployment, and continuous monitoring.
Therefore, enterprises must align their BPA strategy with IT governance, change management, and cybersecurity protocols to avoid fragmentation and associated risks.
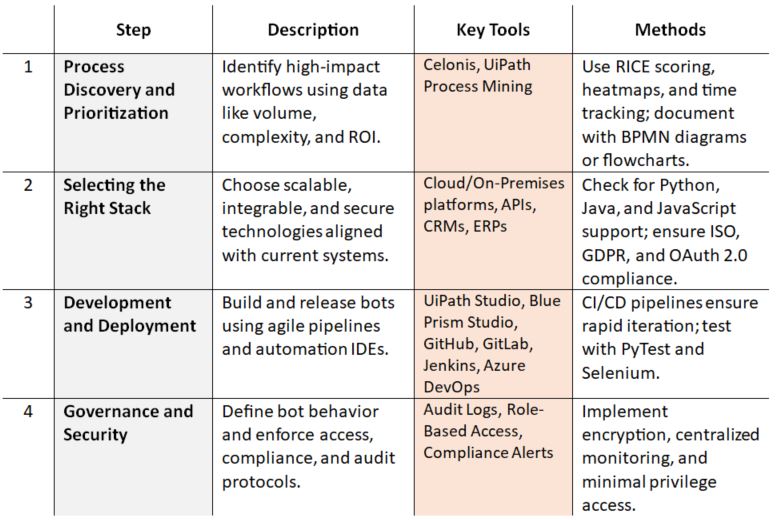
How Does BPA Impact Various Industries? Examples
Let’s shift to the field. How does all this tech translate to actual business results?
Applying automation to departmental key areas yields measurable benefits. These examples demonstrate how businesses can maintain security and compliance while streamlining their operations.
1. Finance
- Invoice Matching: RPA reads invoices, cross-checks purchase orders (POs), and posts entries.
- Fraud Detection: Machine learning models identify anomalies and flag potential risks.
- Reconciliations: Scripts balance books automatically at the end of each month.
2. HR
- Onboarding: Auto-fill documents and route them through e-signature workflows.
- Leave Management: Bots apply company rules and auto-notify stakeholders.
- Payroll: Automation pulls hours, calculates pay, and sends reports.
3. IT Operations
- Ticket Triage: Natural language processing (NLP) bots categorize and assign tickets instantly.
- Patch Management: Schedule and deploy updates using APIs.
- Provisioning: Bots create user accounts across all platforms.
4. Customer Support
- Chatbots: Handle top queries using pre-trained NLP models.
- Priority: Using past behavior, the AI system sends cases to the right team.
- Survey Analysis: A sentiment-scoring survey helps to identify at-risk customers in real-time.
5. Supply Chain
- Order Processing: Automation tools validate orders, update ERP systems, and trigger fulfillment workflows.
- Inventory Management: Integrated BPA tools handle real-time stock updates and restocking alerts.
- Vendor Communication: Bots send auto-reminders, confirm deliveries, and resolve routine queries.
- Logistics Tracking: IoT and automation sync to automatically update shipment status, eliminating the need for manual checks.
The Future of BPA and Its Impacts
Automation is advancing rapidly due to the increasing demand for enterprise systems. Here is what the next chapter holds.
These emerging approaches go beyond simple workflows to deliver adaptive, intelligent, and end-to-end automation.
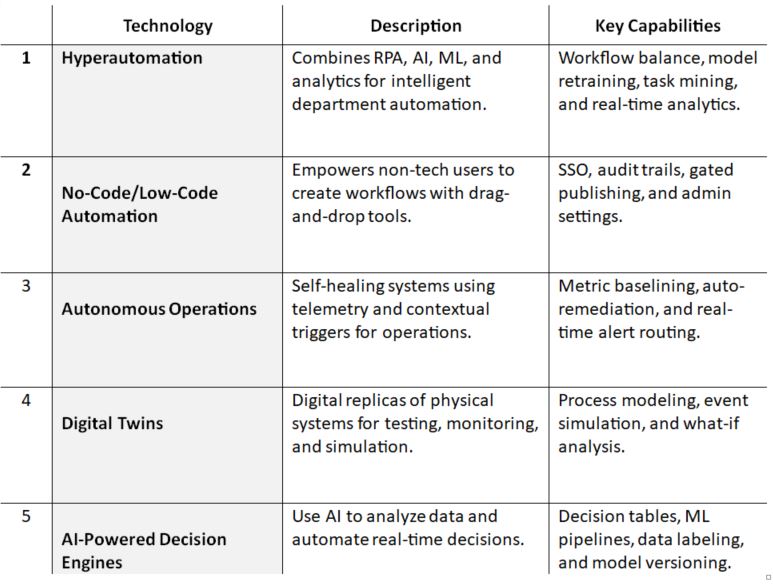
Conclusion
BPA is an umbrella term that encompasses business processes and automation, offering endless possibilities. Start with one method, build the necessary infrastructure, establish governance, test whether the technology or tool works for you, and then expand as needed.
Many BPA-driven tools and software are available in the market; if you want expertise to handle your BPA projects, consider contacting a reliable offshore IT agency specializing in project and scalable technology management.
Related Post
RECOMMENDED POSTS
API-Centric Architecture: The Present & Future of SaaS
06, Feb, 2026
RECOMMENDED TOPICS
TAGS
- artificial intelligence
- agentic ai
- ai
- machine learning
- deepseek
- llm
- saas
- growth engineering
- ai/ml
- chatgpt
- data science
- gpt
- openai
- ai development
- gcp
- sql query
- data isolation
- db expert
- database optimize
- customer expectation
- sales growth
- cloud management
- cloud storage
- cloud optimization
- aws
- deep learning
- modular saas
- social media
- social media marketing
- social influencers
- api
- application
- python
- software engineering
- scalable architecture
- api based architecture
- mobile development
- bpa
- climate change
- llm models
- leadership
- it development
- empathy
- static data
- dynamic data
- ai model
- open source
- xai
- qwenlm
- database management
- automation
- healthcare
- modern medicine
- growth hacks
- data roles
- data analyst
- data scientist
- data engineer
- data visualization
- productivity
- artificial intelligene
- test
ABOUT
Stay ahead in the world of technology with Iowa4Tech.com! Explore the latest trends in AI, software development, cybersecurity, and emerging tech, along with expert insights and industry updates.




Comments(0)
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *